A strong, lustrous, and continuous protein-enriched fiber produced as cocoons by silkworms. These Fibres are further woven into sheen and glossy fabric, which is widely used in the fashion industry for clothing purposes as shirts, trousers, lingerie, silk eye masks, bedcovers, Silk textiles, and much more.
History of Silk:
Silk production first evolved in Neolithic China during Yangshao culture (5000 BC to 3000 BC ). It was refined silk that was first originated by the wife of a Chinese emperor. While having tea, a small cocoon dropped into her hot cup of tea. She was amazed to note that the cocoon disclosed a long fibrous thread. For over 2500 years, the Chinese kept silk production a mystery. Eventually, mulberry silk production evolved in other Asian countries as well.
What is Silk Production?
Silk is a result of the rigorous spinning action of the Bombyx Mori moth. It undergoes four stages of lifecycle:
Egg Larvae Pupae Adult
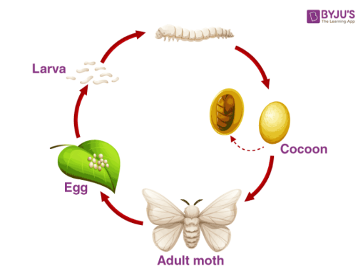
Initially, the moth lays around 500 eggs and dies after that period. The eggs are hatched and raised at a temperature of 65-75 degrees Fahrenheit. After birth, the larvae consume mulberry leaves for a week to put on weight about 10,000 times before.
At this point, the cocoon-spinning action starts, and a liquid called Fibrin is secreted. It hardens on-air contact, and the cocoon gives a protective coating and transfers it into an adult moth. For the harvest of silk, the cocoon collection is termed Reeling.
This reeling process is accelerated by immersing silk cocoons first in hot water. Extracted silk filaments are gathered to form silk Thread and woven into silk fabrics, which can be used as bedsheets, pillowcases, garments, and other fashion hair accessories.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Silk Threads:
The silk filament is durable because of its linear chain of polymers. It contains strong Hydrogen bonds. Under wet conditions, it loses its strength because Hydrogen bonds hydrolyze underwater activity. Chemically, silk threads contain two proteins, sericin and fibroin, in varying proportions. These proteins are responsible for the remarkable quality of silk fabrics. Fibroin gives the smell of burnt hair on heating, whereas sericin is albuminous in nature.
Raw Silk: Understanding the Raw Material
Raw silk fibers are extracted from worm cocoons after being dipped in hot water. The major raw material is the Larvae of the silkworm, which makes the Shell of the cocoons, from which proteinaceous filaments are ejected. One cocoon extracts 1000-2000 feet long silk fibers, whose filaments are packed with fats, wax, salts, and the two main proteins, sericin and fibroin.
Types of Silk:
Naturally produced silk is subdivided into following types:
● Mulberry Silk
● Eri Silk
● Tasar Silk
● Spider Silk
● Sea Silk
Mulberry silk:
It is a luxurious silk derived from the Morus Alba trees of China. The unique thing about mulberry silk is its production and source. Due to its buttery, soft, and velvety luxurious texture, it is termed as King of Silk. This remarkable quality silk contributes to 90% of world silk production. Its glossy, long fibers are used to produce high-fashion clothes and accessories. It is very expensive due to its remarkable quality and intricate processing.
Mulberry silk is extracted from cocoons of a silkworm (Bombyx mori) This moth particularly feeds on the leaves of mulberry trees native to China. This extraordinary diet produces the finest quality silk with a white hue. This type surpasses all the other existing varieties of silk.
Eri silk:
Eri silk worm Samia racini was mainly domesticated in Northeast India, Japan, and China. The main food of these silkworms is Castor plants. Eri silk is white in appearance, and the good thing is that it is extracted without killing silkworms. It depicts outstanding thermal insulation properties, so it is widely used in producing cushions, quilts, blankets, jackets, and shawls.
Tussar silk:
It is silk produced by larvae of silkworms A. paphia and A. assamensis, which belong to the moth genus Antherea. Its main feeding plants are oak and jamun trees. It is highly valued silk with a deep golden colour and fine texture. It finds vast application in fashion clothing, especially Sarreesand, and is a raw material in chemical industries.
Spider silk and Sea silk:
These are the rare and exotic types of natural silk. Spiders release protein-filled fibrous biomaterial. It is a wonderful, flexible material that is tougher than Kevlar and surpasses steel’s strength. It has been widely used in making vilon stings, optical fibers, bandages, and extravagant clothing. Sea silk is obtained as byssus from the foot of pen shells of large marine bivalve mollusks. It is used to make decorative hangings, carpets, and parachutes.
Characteristics of Silk Fabric:
Silk Fabric is termed the Queen of fabrics due to its admirable and incredible characteristics:
● Durability
● Sleek Texture
● Elegant and luxurious appearance
● Breathability
● Thermoregulation activity
● Elasticity
Uses of Silk Fabric
Used for many silk products in the market.
1. Care for Hair
The silk fibers of silk bedding and silk pillowcases have anti-hair breakage properties. They offer less friction to hair and enhance sleep. Moreover, Delicate Silk scrunchies and headbands reduce hair frizz and knots. They also maintain hair hydration, preventing excess surface dryness.
2. Skin benefits
As it is hypoallergenic, it prevents rashes and redness caused by friction during sleep, thereby enhancing sound sleep as well. It is also moisture-wicking and antibacterial, avoiding skin breakouts.
3. Silk Eye Masks:
They help to reduce fine lines, wrinkles, and under-dark circles. Moreover, worldwide research indicates that sleeping with an eye mask promotes deep sleep and blocks light, allowing you to sleep earlier than usual with silk sleep masks.
4. Silk Bedsheets:
They provide frictionless surfaces, moisture-locking properties, and protection from allergens. They create an uninviting environment for dust and bedmates. You would fall asleep better due to the Temperature regulating the activity of the mulberry silk fabric.
5. Industrial uses:
It has versatile furnishing applications such as wall hangings, quilts, rugs, bedding, and couch coverings.
6. Biomaterial:
The extraction of silk proteins is widely used in cell culturing, regenerative medicine production, and bone, cartilage, and tendons healing.
Silk Fabric Trade and Environment

Production and Trade:
The main origin of Silk fabric is China, so the main production and trade were initiated there. In ancient times, it was worn by the upper class only, but with the development of Chinese civilization, the Middle class started affording this fabric. The Chinese Silk Route was established until mid-15th century, which is a connection of Eurasian trade routes.
It was a convoluted web of land and sea paths associating South, Southeast, West Asia, and Southern Europe. Afterwards, the development of the Indus Valley civilization corresponded to Silk cloth production in India between 2450 and 2000 BEC. Silk production is now stretched out towards Korea and Japan in the east to Turkey and Italy in the west.
Environment:
Temperature needs to be controlled in silk farms. Ideal temperature is 23-28 °C and maintained humidity of 65-85%. The climate should maintain the healthy growth of mulberry trees and silkworms.
Silk fabric cost: Factors affecting price:
Silk Fabric is expensive as it requires complicated processing from raw material to finished fabric. Skilled Human labour is required in silk extraction from silkworms, i.e., collecting delicate cocoons, uncoiling them, and weaving them by hand.
Labor costs are extensively high, affecting the final fabric cost. Silk maintains its luxury Fabric status due to quality control practices followed in processing. Silk worm cocoon is the main raw material of the silk industry. Its scarcity tends to increase the end cost of silk fabric.
Caring for Silk Fabric:
It is important to keep the following things in mind:
- If the fabric label says Dry clean, must follow it otherwise gentle hand washing is recommended.
- Do not use bleach, it will damage its delicate fibres
- Use of Mild detergent is highly recommendable
- Spin drying would cause damage and shrinking of silk fabric, so avoid it.
- Exposure to extreme sunlight causes fading of garment
Alternatives to Silk
Synthetic Silk
Artificial silk is obtained from synthetic fibres such as polyester, nylon and rayon. It is an alternative of the natural fiber, silk first developed in 1900s. It is chemically synthesized but extracted from cocoons of insects. Synthetic fibers are polymerized into long chain of silk fibres which are spun into threads and cured with chemicals to maintain shape. It founds application in fashion clothing, bedding and various textile products.
Rayon:
It is a semi-synthetic fiber extracted from the cellulose of wood and other agricultural products. It is highly breathable, viscose, and cheap alternative to the natural fiber-produced Silk. It imparts cool and comfortable feeling on the skin and is widely used to make clothing, bedding, and blankets.
Plant-Based Alternatives
Processing of plant-based sources obtain plant-based Silk. Appealing textured and plant-based alternatives to Silk have been produced, which are cruelty-free and sustainable. Vegan Silk tends to be more breathable and hypoallergenic wear silk. They may include soy silk, bamboo silk, eucalyptus silk.
Bamboo Silk
It is an amazing alternative to traditional Silk, mainly extracted from the roots of bamboo plants. Its lightweight and softness make it a good option for clothing such as skirts, shirts, scarves, and lingerie.
Conclusion
Silk and silk alternatives are economically beneficial due to their smooth texture, durability, and strength of fabric. Outstanding silk apparel items such as ties, scarves, blouses, skirts, and shirts are produced in the fashion industry. The demand for silk garments is increasing, and the silk market is expected to be worth US$20.0 billion in 2024.
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions about Silk:
Is Silk sustainable and environmentally friendly?
Yes, it is considered the most sustainable and environmentally friendly fabric. It is naturally biodegradable and implies less chemical use. Obtained from silkworms, it is highly renewable. It is environment-friendly due to its least impact upon water, air, or land. Moreover, it is free from fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. It can be easily recycled and turned into polymeric fabric. While doing so, it doesn’t release any microplastics into the environment.
Is Silk more delicate than other fabrics?
Yes, it is a delicate, soft fabric that must be used with care. Gentle washing and proper drying are advisable.
What makes Silk so unique?
Silk is well known for its unique cultivation process from the cocoons of silkworms. After steps of complicated processing, the end result is a silk fabric with an all-natural sheen and glimmer.
Is Silk for summer or winter?
Silk can be worn in any weather, but its lightweight and hydrophobic qualities make it more suitable for your summer closet.







